HertzBeat v1.4.0 released, cluster is coming!
What is HertzBeat?
HertzBeat is an open source, real-time monitoring system with custom monitoring, high performance cluster and agentless capabilities.
Features
- Combines monitoring, alarm, and notification features into one platform, and supports monitoring for web service, program, database, cache, os, webserver, middleware, bigdata, cloud-native, network, custom and more.
- Easy to use and agentless, offering full web-based operations for monitoring and alerting with just a few clicks, all at zero learning cost.
- Makes protocols such as
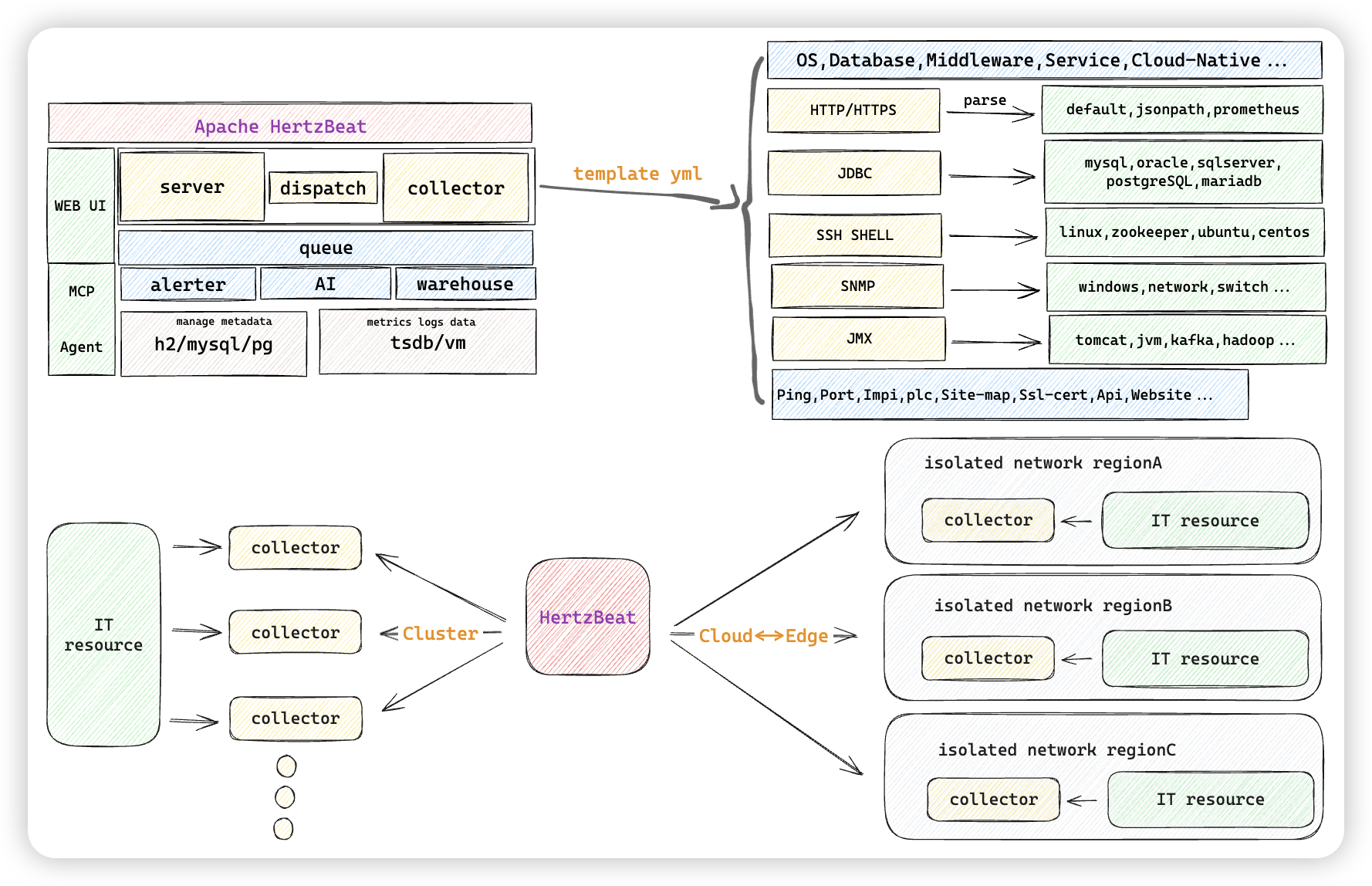
Http, Jmx, Ssh, Snmp, Jdbc, Prometheusconfigurable, allowing you to collect any metrics by simply configuring the templateYMLfile online. Imagine being able to quickly adapt to a new monitoring type like K8s or Docker simply by configuring online with HertzBeat. - High performance, supports horizontal expansion of multi-collector clusters, multi-isolated network monitoring and cloud-edge collaboration.
- Provides flexible alarm threshold rules and timely notifications delivered via
DiscordSlackTelegramEmailDingDingWeChatFeiShuWebhookSMS.
HertzBeat's powerful customization, multi-type support, high performance, easy expansion, and low coupling, aims to help developers and teams quickly build their own monitoring system.
Github: https://github.com/apache/hertzbeat
Gitee: https://gitee.com/hertzbeat/hertzbeat
The cluster version is coming
Our previous hertzbeat has always been a stand-alone version. The component code is modular but does not support the independent deployment of the collector. The upper limit of the number of monitoring supported is naturally limited by a single node, and it cannot cope with the unified management of resources in multiple isolated networks. After more than a month of iterations, we rewrote the collection task scheduling, deployed the collectors independently, and designed the stand-alone version and the cluster version to use the same set of codes to facilitate subsequent maintenance and upgrades. The two modes of the stand-alone cluster can be switched without perception. In the end, I am very happy that the cluster version met with you as scheduled.
The cluster version not only brings us more powerful monitoring performance, but also has functions such as cloud-side collaboration that are full of imagination.
High performance cluster
- Supports the deployment of collector clusters, multi-collector clusters scale horizontally, and exponentially improves the number of monitors and collection performance.
- The monitoring task is self-scheduled in the collector cluster. A single collector hangs up and migrates the collection task without perceptual failure. Newly added collector nodes are automatically scheduled to share the collection pressure.
- It is very convenient to switch between stand-alone mode and cluster mode and deploy without additional components.
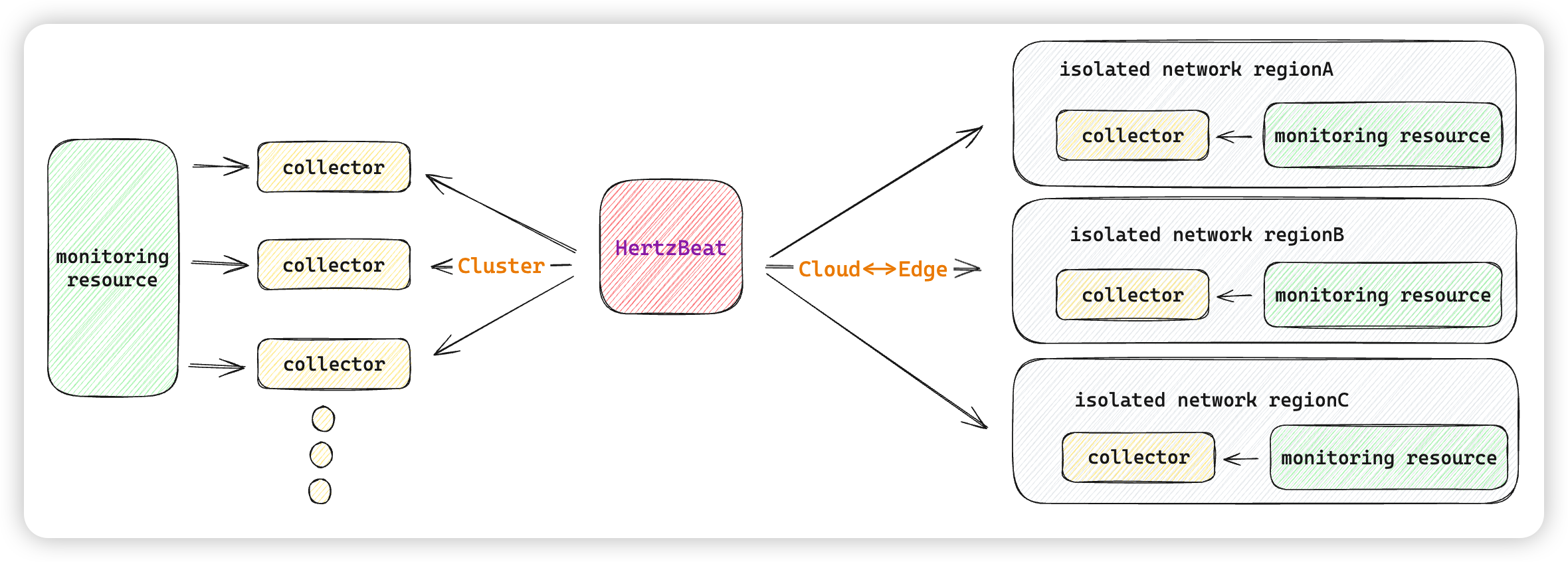
Cloud Edge Collaboration
Support the deployment of edge collector clusters, and cooperate with the main HertzBeat service cloud to improve collection capabilities.
In the isolated network where multiple networks are not connected, in the previous solution, we needed to deploy a monitoring system on each network, which resulted in the incompatibility of data and inconvenient management, deployment and maintenance. HertzBeat provides cloud-edge collaboration capabilities. Edge collectors can be deployed on multiple isolated networks. When monitoring is added, collectors are specified. The collectors collect monitoring tasks within the isolated network, and report the collected data. The main HertzBeat service performs unified scheduling, management and display. This is mostly used in unified monitoring scenarios of multiple isolated data centers or cloud resources and resources under the cloud of different vendors.

Why open source cluster version?
Often, some strategies for making open source products that need to be commercialized will be to use the stand-alone version as a toy for the beginners of small players, and then use the cluster version as a closed-source product for paid players who need it. This model can be said to be very good and worthy of recognition, that is, to ensure that open source can also get benefits, and it is also applicable to the development strategy of many open source projects, and it may be more smooth on the business path. Some people on the Internet will sneer at such open source projects that are divided into stand-alone and cluster versions, thinking that they are pseudo-open source, and open source is a gimmick. They think that open source should be open source and free, and the open source team should contribute everything selflessly. . . . Very speechless people like this, there is only return for investment. When you use open source software for free and get value, should you think about what you have paid for open source software instead of just asking for it. So back to the topic, why do we want an open source cluster version? Just because you love open source? If you say that we are still teenagers, you may believe this, but do you believe this when a person who is going to be 30 and has family responsibilities says this, I don’t believe it myself😂. First of all, let's take a look at what open source can bring, or why open source should be done. The idea of full-time open source at the beginning is very simple, to make your favorite open source product (realized), the programmer's dream can be deployed on thousands of servers (see the downloads have been realized), and then make money based on this open source product ( not crying yet).
- User traffic. Open source projects are provided free of charge to users and developers, and have advantages in attracting users to use and promoting them.
- User trust. Open source products are naturally easy to gain the trust and patience of users, or lower the threshold of trust for users.
- Community collaboration. Open source products can attract top contributors to contribute together, receive user feedback issues, pr contributions, etc.
- Driven by the community, open source projects will become better and better, and more people will participate and use them after positive feedback. Community collaboration I think this is the meaning of open source, and this is not just the contribution code collaboration between programmers, users are all collaboration objects (for example, our project has a large number of operation and maintenance friends who contribute code and documents), if it is only code Open source without community collaboration, it is better to release an installation package for others to use and download for free.
- Product ecology. This is required for some ecological products, such as hertzbeat, which need to support monitoring types that connect to various types of protocols, and a large number of monitoring templates. Only a good open source project ecology can attract other contributors to contribute and share, exchange what is needed in the ecology, and ultimately everyone will benefit from the ecology. This is difficult to do in closed source programs.
The above points focus on community collaboration and product ecology. This is also the reason for the open source cluster version. Only open source products can be rolled into stronger product power. For example, the technical feature of cluster will naturally attract developers (and the cluster itself is The product of our community collaboration) will attract more users and contributors to use feedback and iterate together. The community drives and then positively promotes open source projects and satisfies user functional experience. As for open source commercialization, the premise of open source commercialization is to have a really good, popular, and widely used open source product, and then do commercialization on this basis to make money.
Install quickly via docker
-
Just one command to get started:
docker run -d -p 1157:1157 -p 1158:1158 --name hertzbeat apache/hertzbeator use quay.io (if dockerhub network connect timeout)docker run -d -p 1157:1157 -p 1158:1158 --name hertzbeat quay.io/tancloud/hertzbeat -
Access
http://localhost:1157to start, default account:admin/hertzbeat -
Deploy collector clusters
docker run -d -e IDENTITY=custom-collector-name -e MANAGER_IP=127.0.0.1 -e MANAGER_PORT=1158 --name hertzbeat-collector apache/hertzbeat-collector-e IDENTITY=custom-collector-name: set the collector unique identity name.-e MANAGER_IP=127.0.0.1: set the main hertzbeat server ip.-e MANAGER_PORT=1158: set the main hertzbeat server port, default 1158.
Detailed config refer to Install HertzBeat via Docker
What's Changed
Welcome to explore more new version updates, thanks to the hard work of the community partners, love 💗!
- [doc] add v1.3.2 publish doc by @tomsun28 in https://github.com/apache/hertzbeat/pull/1075
- remove elasticsearch unused param index by @Ceilzcx in https://github.com/apache/hertzbeat/pull/1080
- feature support monitoring apache airflow by @luoxuanzao in https://github.com/apache/hertzbeat/pull/1081
- add luoxuanzao as a contributor for code by @allcontributors in https://github.com/apache/hertzbeat/pull/1083
- [collector] bugfix sshd cannot use private key to connect by @gcdd1993 in https://github.com/apache/hertzbeat/pull/1084
- bugfix update dashboard alerts cards height not consist by @tomsun28 in https://github.com/apache/hertzbeat/pull/1087
- Feature#serverchan by @zqr10159 in https://github.com/apache/hertzbeat/pull/1092
- bugfix dm database monitoring connect error by @lisongning in https://github.com/apache/hertzbeat/pull/1094
- add lisongning as a contributor for code by @allcontributors in https://github.com/apache/hertzbeat/pull/1096
- update alert rule operator display "<=" to ">=" by @Ceilzcx in https://github.com/apache/hertzbeat/pull/1097
- [doc] add custom monitoring relate document by @tomsun28 in https://github.com/apache/hertzbeat/pull/1098
- add YutingNie as a contributor for code by @allcontributors in https://github.com/apache/hertzbeat/pull/1103
- Remove unreachable status by @YutingNie in https://github.com/apache/hertzbeat/pull/1102
- 139 auto update alert status by @l646505418 in https://github.com/apache/hertzbeat/pull/1104
- feat: aviator fn for str contains, exists & matches by @mikezzb in https://github.com/apache/hertzbeat/pull/1106
- add mikezzb as a contributor for code by @allcontributors in https://github.com/apache/hertzbeat/pull/1107
- bugfix common alarm do not need monitorId tag existed by @tomsun28 in https://github.com/apache/hertzbeat/pull/1108
- bugfix extern alert do not have labels mapping inner monitor by @tomsun28 in https://github.com/apache/hertzbeat/pull/1111
- feature: support apache spark metrics monitoring by @a-little-fool in https://github.com/apache/hertzbeat/pull/1114
- add a-little-fool as a contributor for code by @allcontributors in https://github.com/apache/hertzbeat/pull/1116
- [Feature]Add third report of TenCloud by @zqr10159 in https://github.com/apache/hertzbeat/pull/1113
- [Feature]Add third report of TenCloud (#1113) by @zqr10159 in https://github.com/apache/hertzbeat/pull/1119
- [manager] fix: can query by tags when tagValue is null by @l646505418 in https://github.com/apache/hertzbeat/pull/1118
- bugfix the notification template environment variable display error by @tomsun28 in https://github.com/apache/hertzbeat/pull/1120
- add littlezhongzer as a contributor for code by @allcontributors in https://github.com/apache/hertzbeat/pull/1127
- feature:monitor brearer token api, ignore letter case to comparison by @littlezhongzer in https://github.com/apache/hertzbeat/pull/1122
- docs: enhance README by @mikezzb in https://github.com/apache/hertzbeat/pull/1128
- Update app-oracle.yml by @ChenXiangxxxxx in https://github.com/apache/hertzbeat/pull/1129
- add ChenXiangxxxxx as a contributor for code by @allcontributors in https://github.com/apache/hertzbeat/pull/1130
- fix alarm silence strategy setting failed by @Ceilzcx in https://github.com/apache/hertzbeat/pull/1131
- support run sql script file in jdbc protocol config by @tomsun28 in https://github.com/apache/hertzbeat/pull/1117
- bugfix return old cache json file when upgrade version by @tomsun28 in https://github.com/apache/hertzbeat/pull/1137
- support ssh protocol config choose if reuse connection by @tomsun28 in https://github.com/apache/hertzbeat/pull/1136
- feat(web): alert threshold UI support matches & contains by @mikezzb in https://github.com/apache/hertzbeat/pull/1138
- support hertzbeat metrics collector cluster by @tomsun28 in https://github.com/apache/hertzbeat/pull/1101
- add collector card in dashboard by @tomsun28 in https://github.com/apache/hertzbeat/pull/1147
- bugfix: linux collect warning: bad syntax, perhaps a bogus '-' by @Mr-zhou315 in https://github.com/apache/hertzbeat/pull/1151
- add Mr-zhou315 as a contributor for code by @allcontributors in https://github.com/apache/hertzbeat/pull/1157
- support config timezone locale language region on web ui by @tomsun28 in https://github.com/apache/hertzbeat/pull/1154
- bugfix monitoring template app name already exists by @tomsun28 in https://github.com/apache/hertzbeat/pull/1152
- bugfix can not startup when error monitoring template yml file by @tomsun28 in https://github.com/apache/hertzbeat/pull/1153
- tags also deleted when the monitor is deleted by @Ceilzcx in https://github.com/apache/hertzbeat/pull/1159
- monitoring param host with http head will not be error reported by @littlezhongzer in https://github.com/apache/hertzbeat/pull/1155
- [script] feature update build.sh and Dockerfile: detect app version a… by @XimfengYao in https://github.com/apache/hertzbeat/pull/1162
- add XimfengYao as a contributor for code by @allcontributors in https://github.com/apache/hertzbeat/pull/1163
- [doc] add collector clusters document by @tomsun28 in https://github.com/apache/hertzbeat/pull/1161
- [hertzbeat] release hertzbeat version v1.4.0 by @tomsun28 in https://github.com/apache/hertzbeat/pull/1168
⛄ Supported
- Site Monitor, Port Availability, Http Api, Ping Connectivity, Jvm, SiteMap Full Site, Ssl Certificate, SpringBoot, FTP Server
- Mysql, PostgreSQL, MariaDB, Redis, ElasticSearch, SqlServer, Oracle, MongoDB, Damon, OpenGauss, ClickHouse, IoTDB, Redis Cluster
- Linux, Ubuntu, CentOS, Windows
- Tomcat, Nacos, Zookeeper, RabbitMQ, Flink, Kafka, ShenYu, DynamicTp, Jetty, ActiveMQ
- Kubernetes, Docker
- Huawei Switch, HPE Switch, TP-LINK Switch, Cisco Switch
- and more for your custom monitoring.
- Notifications support
DiscordSlackTelegramMailPinningWeChatFlyBookSMSWebhook.
Github: https://github.com/apache/hertzbeat Gitee: https://gitee.com/hertzbeat/hertzbeat